L1/ L2 Regularization
From Bayes perspective, regularization is to add a prior knowledge to the model. For example, L2 is similar to add a gaussian distribution prior with . When , it means no regularization, then in the other words, we can treat it as covariance is infinite; when , then convirance is to zero, then the variance of the parameters in the model is small, consequently, the model is more stable.
What's L1 and L2 regularization
L2 is the sum of the sure of the weights L1 is the sum of the absolute values.
What's the difference between L1 and L2?
L2 has unique solutions and L1 have multiple solutions. see the following picture.
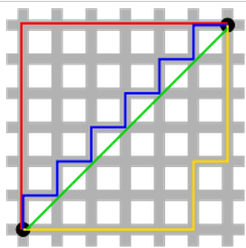
R: http://www.chioka.in/differences-between-l1-and-l2-as-loss-function-and-regularization/
Why L1 regularization can generate sparsity?
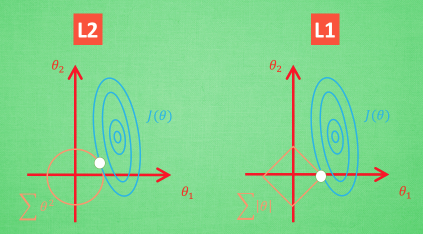
We can use this graph is explain. We have two parameters,theta1 and theta2.
The error value is the same for each blue circle. Regularization terms show in yellow. The first point the blue lines meet yellow line is the optimal solution.
You can see that, for L1, the meeting point mostly happens at the corner while L2 doesn't have corner. 
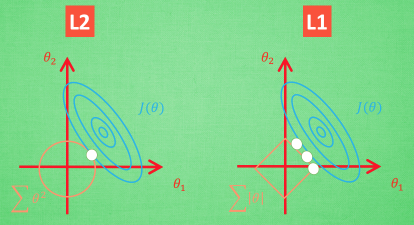
Why L1 is not stable?
??????? need help
What's the L1 and L2 loss?
L1 loss is least sum of absolute deviation L2 loss is least sum of square of the difference tween the target value and the estimated values.
What's the difference between L1 and l2 as a loss function?
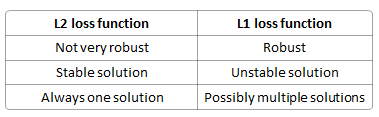
R: http://www.chioka.in/differences-between-l1-and-l2-as-loss-function-and-regularization/
Why L1 is more robust?
Least absolute deviations is robust in that it is resistant to outliers in the data. LAD gives equal emphasis to all observations, in contrast to OLS which, by squaring the residuals, gives more weight to large residuals, that is, outliers in which predicted values are far from actual observations. This may be helpful in studies where outliers do not need to be given greater weight than other observations. If it is important to give greater weight to outliers, the method of least squares is a better choice.